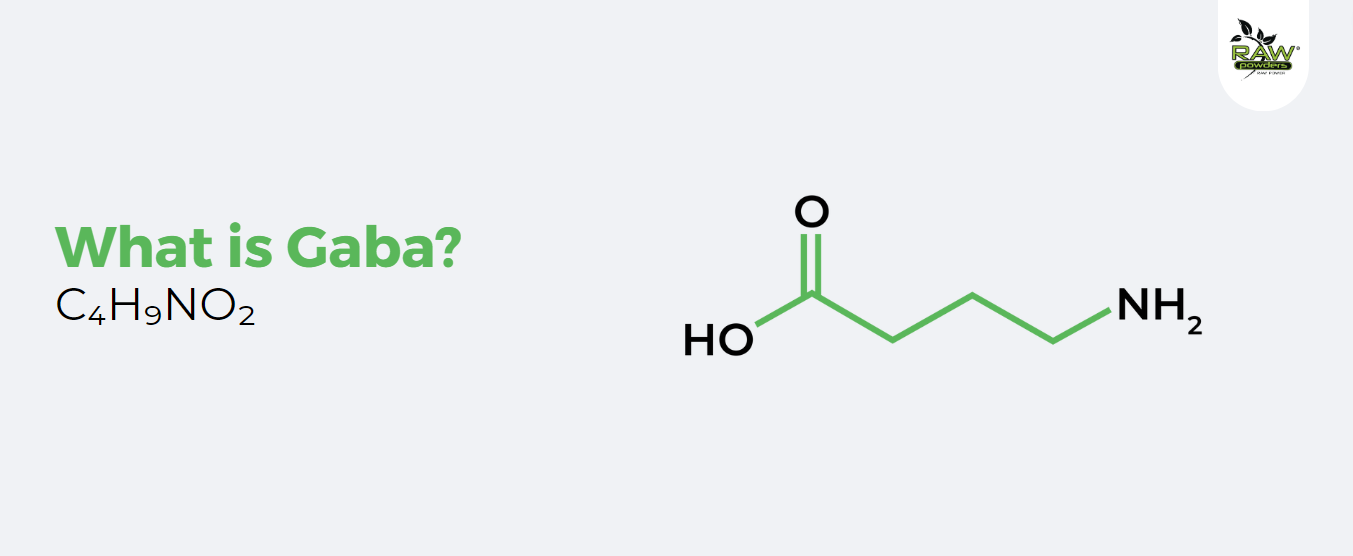
WHAT IS GABA?

GABA, or gamma-aminobutyric acid, also known as gamma-amino butyric acid, is an important neurotransmitter in the human brain. It is a compound that plays a key role in transmitting signals between brain cells, or neurons. Its main function is to regulate neuronal hyperactivity, which means that it stops or slows the transmission of nerve impulses. This is important because GABA contributes to the balance between inhibitory and excitatory (activating) neurotransmitters in the brain, and this balance is important for normal brain function.
GABA acts as an inhibitor in the brain, which means that it reduces neuronal activity. This can help to reduce arousal, and GABA is also involved in some central nervous system functions such as relaxation, calmness and sleep.
How does GABA work?
GABA is a natural amino acid synthesised from glutamate in brain cells. The role of GABA is to prevent glutamate, the main carrier of excitability, from overwhelming you. Too much glutamate can cause a seizure, while too much GABA can cause a coma. In a healthy brain, a critical balance of GABA and glutamate is maintained.
It is estimated that 40% of the synapses in the human brain work with GABA and therefore contain GABA receptors.
During stress, GABA acts as a "brake" on neuronal circuits. Too low levels of GABA can cause anxiety, insomnia, low mood and worry.
GABA improves normal sleep cycles and blood pressure. GABA stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete human growth hormone, and it helps produce endorphins, which help you feel good after exercise or sex.
When GABA levels in the brain are normalised, anxiety, insomnia, nervousness, restlessness, blood pressure and stress are reduced. Did you know that antidepressants (benzodiazepines) such as Valium and Xanax work by increasing the sensitivity of GABA receptors?
The importance of GABA for the body
1. Calmness and Relaxation: Because of its inhibitory properties, GABA can help you relax and reduce stress.
2. Sleep Quality: GABA can also help improve sleep quality by regulating brain states that are associated with sleep.
3. Pain Regulation: GABA can regulate pain by modulating pain signals between the brain and the nervous system.
GABA and Health
Without sufficient levels of GABA, people can experience a range of health problems such as anxiety, depression, poor sleep, and even epilepsy. As a result, some medications containing GABA and GABA supplements can be used to treat or manage these conditions. Read more about the benefits of GABA supplements here.
Biology and action
GABA has several receptor protein families, including GABA(A) and GABA(B) receptors. The GABA(A) receptor is an ion channel that, when bound to GABA, allows chloride ions to enter the neuron, reducing its electrical activity. In contrast, the GABA(B) receptor is a G-protein coupled receptor that modulates other ion channels and may influence neuronal activity through several mechanisms.
Neurophysiology
GABA plays an important role in neurophysiology. It modulates neuronal excitability and contributes to information transmission and processing in the brain. In addition, GABA gives the neuronal network the ability to modulate its responses to external stimuli and is involved in a wide range of cognitive functions, including learning, memory, and attention.
GABA and Neuroplasticity
GABA also plays an important role in neuronal plasticity, i.e. the ability to form new connections within a neuronal network. Too much or too little GABA activity can affect the ability of a neural network to adapt to change and learn new things.
GABA and Mood
Given the important role of GABA in brain function, its level and activity in the brain can have a significant impact on mood and emotional states. For example, GABA imbalances are associated with some mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety, and can influence stress responses and behaviour.
How do GABA receptors in the brain work?
There are two natural GABA signalling receptors in nerve cells - the GABA-A receptor and the GABA-B receptor. Although each acts differently, when GABA binds to one of these receptors, the response of the nerve cell is reduced. This means that GABA modulates the signals sent by nerve cells.
GABA contributes to brain health and function in several ways. However, two in particular stand out:
2. As one of the two main inhibitory neurotransmitters, GABA works by preventing anxiety-related nerve signals from reaching other neurons. It does this by binding to receptors that would otherwise excite those neurons. Over-excitation of neurons in certain areas of the brain causes anxiety-related symptoms.
A study conducted by Japanese researchers on 8 volunteers who had to cross a high-hanging bridge showed that GABA can enhance stress resilience by acting as a natural relaxant, and that its effects could be observed within 1 hour of taking GABA. Subjects taking placebo had significantly elevated markers of the stress hormone in their blood, whereas subjects taking GABA had significantly lower levels of the same markers.
2. GABA also helps to reduce beta brain waves and increase alpha brain waves. Beta brain waves are important for attention, alertness, concentration and memory development. However, excessive levels of concentration, especially during times of stress, can lead to anxiety, depression, insomnia and even more stress.
When you are alert, both Alpha and Beta brain waves can be stimulated. However, the type of alertness determines which brainwave is produced.
Alertness in an Alpha wave state is associated with a state of relaxation. In contrast, a state of alertness under stress produces a Beta wave. However, an excess of Beta brain waves contributes to a variety of neural disorders, including anxiety and stress.
Sources of GABA
- Micro-organisms: GABA can be produced by the fermentation process of micro-organisms, e.g. using Lactobacillus bacteria.
- Food: Some foods are natural sources of GABA, e.g. rice, bran, black tea leaves, avocados, turkey, eggs, nuts and seeds.
Synthetic GABA supplements are chemically engineered and produced in laboratories.
GABA supplements are usually available in tablet, capsule or powder form. It is important to read the recommendations for use and consult a healthcare professional before taking GABA supplements. Read more about the dosage and experiences with GABA supplements here.
GABA is a critical component of the brain, playing an essential role in regulating neuronal activity and ensuring the stability and balance of brain networks. Its activity is complex and multifunctional, with important consequences for cognitive function, emotional states, and adaptation to the environment. It is important to note that GABA supplementation may cause side effects, read more about this here.





_front%20(1)-250x250.png)



_front%20(1)-250x250.png)

-(NN)_front%20(1)-min-250x250.png)

_front%20(1)-250x250.png)


_front%20(1)-min-250x250.png)
_front%20(1)%20(1)-250x250.png)
_front%20(1)-250x250.png)












-250x250.png)

